Many U.S. citizens have overseas financial accounts for various legitimate reasons. Since most of those foreign financial institutions are not subject to the same reporting requirements as U.S. institutions, the Treasury Department requires a Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR) to be filed each year. Not all taxpayers, however, are required to submit the annual report. Keep reading to learn more about who has to file, as well as when and how to submit the report.
The Bank Secrecy Act
In 1970, the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), also known as the Currency and Foreign Transactions Reporting Act, was created to help prevent criminals from using financial institutions to hide or launder money obtained through illegal activities. Under BSA, banks and other financial institutions must provide documentation to regulators whenever there are suspicious cash transactions of $10,000 or more. The U.S. government also uses the BSA to require annual filing of the FBAR. This report helps identify taxpayers who may be hiding unreported income maintained or generated abroad, as well as money obtained through illicit activities.
Who Must File the FBAR?
Any U.S. person with a financial interest or signature authority on a financial account outside the United States that has an aggregate maximum value that exceeds $10,000 at any time during the calendar year must file an FBAR. In this case, a U.S. person includes:
- U.S. citizens and residents
- Entities created or organized in the U.S., such as corporations, partnerships, and limited liability companies (LLC)
- Trusts formed under U.S. laws
- Estates formed under U.S. laws
If two people jointly maintain an account, or several persons own a partial interest, each U.S. person would be required to report the entire value of the account on an FBAR.
Spouses who have interests in foreign accounts must both file the FBAR unless the following conditions are met: (1) all the financial accounts that the non-filing spouse is required to report are jointly owned with the filing spouse; (2) the filing spouse reports the jointly owned accounts on a timely filed FBAR electronically signed (PIN) in item 44; and (3) the filers have completed and signed Form 114a, Record of Authorization to Electronically File FBARs.
A person’s income tax filing status does not affect their requirement to submit the report. In fact, U.S. persons who are not required to file federal income taxes may still be required to file an FBAR.
Which Financial Accounts Are Included?
A financial account is foreign if it is located outside of the United States and/or its territories. Here are some examples of accounts that would require the FBAR:
- Bank accounts (checking, savings, and CDs)
- Security accounts
- Commodity futures or options accounts
- Cash-Value insurance policies
- Mutual funds
Accounts maintained with financial institutions located on U.S. military bases outside of the United States are exempt from FBAR.
How to Determine Account Value
To determine the aggregate maximum value for foreign accounts, you will need to convert the value into U.S. dollars using the exchange rate on the last day of the calendar year.

When to File the FBAR
The FBAR is due by April 15 each year, following the calendar year reported. If you fail to meet that date, you will receive an automatic filing extension to October 15. Those impacted by natural disasters may receive additional time to submit the report.
If you do not file as required, you may be subject to monetary and/or criminal penalties. Current civil monetary penalty maximums are as follows:
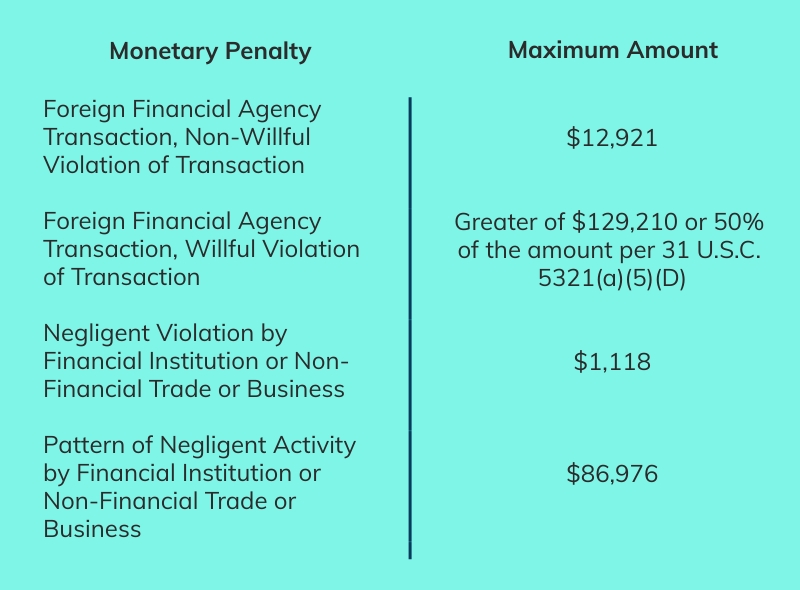
Willfully failing to file or retain records, or filing a false FBAR, can lead to criminal penalties that include fines up to $500,000 or time in prison (5 to 10 years).
How to File the FBAR
The FBAR is not filed with your federal income tax return. It must be submitted electronically through the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network’s BSA e-filing network. If you are unable to file online and want to submit a paper report, you will need to contact the FinCEN’s Regulatory Helpline at 800-949-2732 to request an exemption. If approved, they will mail you instructions and the paper form to complete.
You should keep records of any accounts reported on the FBAR for at least five years. The records should include:
- Name on the account
- Account number or designation
- Financial institution address/contact information
- Type of account
- Maximum value of the account for the reporting period
Officers and employees who file the FBAR to report signature authority for an employer are not required to personally retain records for those accounts.
For additional questions or assistance with the FBAR, please call the IRS FBAR Hotline at 866-270-0733. You can also schedule a free consultation with Tax Defense Network by calling 855-476-6920.
